China’s Green Development in the New Era
The State Council Information Office of the People’s Republic of China
January 2023
Contents
Preface 1
I. Staying Firmly Committed to Green Development 3
II. A Basic Green Territorial Configuration Is in Place 7
III. Adjusting and Improving the Industrial Structure 20
IV. Extensive Application of Green Production Methods 25
V. Eco-Friendly Living Becomes the Prevailing Ethos 35
VI. Improving the Institutions and Mechanisms for
Green Development 38
VII. Building the Earth into a Beautiful Home 43
Conclusion 47
Preface
Green is the color of nature and the symbol of life. A sound eco-
environment is the basic foundation for a better life, and the common
aspiration of the people. Green development is development that follows
the laws of nature to promote harmonious coexistence between humanity
and nature, development that obtains the maximum social and economic
benefits at minimum cost in resources and environmental impact, and sus-
tainable and high-quality development that protects the eco-environment.
It has become the goal of all countries.
Respecting and protecting nature has made an important contribu-
tion to the survival and prosperity of the Chinese nation over thousands
of years. The concept of “harmony between humanity and nature” is a
distinct characteristic of Chinese civilization. To vigorously promote the
building of a socialist eco-civilization, China has established a fundamen-
tal national policy of conserving resources and protecting the environ-
ment, and a national strategy of sustainable development since the launch
of reform and opening up.
Since the 18th CPC National Congress in 2012, under the guidance of
Xi Jinping Thought on Socialism with Chinese Characteristics for a New
Era, China has firmly upheld the belief that lucid waters and lush mountains
are invaluable assets. It has prioritized eco-environmental conservation
and green development, promoted the comprehensive green transforma-
tion of economic and social development, and achieved modernization
based on harmony between humanity and nature. Wonders have been ac-
complished in eco-environmental protection and green development, and
great strides have been made in building a beautiful China. Green is the
defining feature of China in the new era and green development features
the Chinese path to modernization. With more blue skies, green moun-
tains, and lucid waters, the Chinese people could enjoy more accessible
and sustainable green benefits. China’s green development has helped to
expand the greening areas of its own land and the earth, benefitting both
China and the world at large.
As the world’s largest developing country, China is committed to
the idea of a global community of shared future. It has offered unwaver-
ing support to multilateralism, proposed the Global Development Initia-
tive and the Global Security Initiative, expanded practical cooperation,
and actively participated in global environment and climate governance.
It has contributed Chinese wisdom and strength to implementing the UN
2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, creating a community of life
for humanity and nature, and building a clean, beautiful and prosperous
world of sustainable development.
The Chinese government is publishing this white paper to present a
full picture of China’s ideas, actions, and achievements in green develop-
ment in the new era, and to share with the world its experience in this re-
gard.
I. Staying Firmly Committed to
Green Development
To meet the people’s desire for a better life, China has treated lucid
waters and lush mountains as invaluable assets and worked to maintain
harmony between humanity and nature in its development. China favors
high-quality economic growth, high-level environmental protection, and
a path of sound development based on higher economic output and living
standards, and healthy ecosystems.
1. Applying a people-centered development philosophy
The people-centered philosophy is a governing principle of the Com-
munist Party of China (CPC), and a sound eco-environment is the fairest
public product and the most inclusive public benefit. As China’s moderni-
zation advances and living standards improve, the popular demand for a
beautiful environment is growing. In the people’s happiness index, the
weight of environment has increased. To meet the growing demand for a
beautiful environment, China has strengthened eco-environmental conser-
vation and protection and vigorously promoted eco-friendly ways of work
and life. It has focused on solving the major environmental problems that
seriously endanger people’s health, improved the quality of the environ-
ment and ecosystems, and provided more quality eco-environmental
goods, so as to help people feel happier, more satisfied, and more secure
in a beautiful environment.
2. Focusing on sustainable development in China
Society will prosper when the environment improves, and lose vigor
as the environment degrades. Nature provides the basic conditions for
human survival and development. Respecting, accommodating, and
protecting nature is essential for sustainable development. Bearing in
mind that its environmental capacity is limited and its ecosystem is
fragile, China has not only pursued development for the present genera-
tion, but also mapped out plans for generations to come. It regards eco-
environmental conservation as fundamental to sustainable development in
China. It values both the environment and economic development, works
to translate eco-environmental strengths into development strengths, and
always looks to realize the economic and social value that lucid waters
and lush mountains have, which will bring about financial returns, eco-
environmental benefits, social benefits, and harmony between humanity
and nature.
3. Applying systems thinking and a coordinated approach
Green development is an all-round revolutionary change in our
values, and in how we work, live, and think. China has applied systems
thinking to the whole process of economic and social development and
eco-environmental conservation and protection. It has taken a sound ap-
proach to the relationships between development and protection, between
overall and local interests, and between the present and the future. It has
taken a scientific, moderate, and orderly approach to the use of territorial
space, and promoted a sound economic structure that facilitates green,
low-carbon, and circular development. It has fostered an institutional sys-
tem that combines both constraints and incentives to coordinate industrial
restructuring, pollution control, eco-environmental conservation, and
climate response. China has endeavored to cut carbon emissions, reduce
pollution, expand green development, and pursue economic growth. It has
prioritized eco-environmental protection, conserves resources and uses
them efficiently for green and low-carbon development. It has developed
spatial configurations, industrial structures, and ways of work and life
that help conserve resources and protect the environment, and promoted
greener economic and social development in all respects.
4. Working together for global sustainable development
Protecting the environment and countering climate change are the
common responsibilities of all countries. Only when all countries unite
and work together to promote green and sustainable development can we
maintain the overall balance in the earth’s ecology and protect humanity’s
one and only home. China has shouldered its responsibilities, actively
participated in global environmental governance, and pledged to reach

carbon emissions peak by 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2060. It will
advance the green transition with these goals as the lead, play a more
active part in bilateral and multilateral international cooperation on green
development, promote a fair and equitable system of global environmental
governance, and contribute its wisdom and strength to global sustainable
development.
II. A Basic Green Territorial
Configuration Is in Place
China is making efforts to optimize its governing system of territo-
rial space. The country has strengthened the overall planning and coordi-
nated management and control of territorial space for working and living
and for the environment. It has intensified efforts to protect and restore
ecosystems, effectively expanded the capacity of the eco-environment,
and promoted the rapid accumulation of natural wealth and eco-environ-
mental wealth, leading to historic, transformative, and comprehensive
changes in eco-environmental protection and providing strong support for
the sustainable and healthy development of the economy and society.
1. Optimizing the development and protection of territorial space
A country’s territorial space is the carrier for green development.
China has implemented a functional zoning strategy and established a
unified territorial space planning system that is science-based, efficient
and built upon clearly defined powers and responsibilities. Taking into
consideration factors such as population distribution, regional economic
structures, land use, and eco-environmental protection, it has planned
for the development and protection of territorial space with a holistic ap-
proach, so as to achieve higher-quality and more sustainable development
of its territorial space.
China has integrated different plans into a single master plan for ter-
ritorial space development. It has integrated functional zoning, land use,
urban and rural planning, and other spatial planning into a unified territo-
rial space plan. A comprehensive system integrating planning approval,
implementation supervision, regulations, policies and technical standards
is taking shape. The role of territorial space planning has been strength-
ened in guiding and constraining various specific plans. It has sped up the
drafting of various plans for territorial space at all levels. As a result, an
overall master plan will eventually be drawn up for the development and
protection of territorial space.
Concerted efforts have been made to optimize the use of territorial
space. Based on the results of national land resource surveys, China has
carried out an evaluation of the carrying capacity of resources and the
environment, and suitability of land development. It has scientifically
designated agricultural, ecological, urban and other functional zones, and
improved the territorial space layout that consists of three major zones
– main agricultural production zones, key ecosystem service zones and
urbanized zones. To strengthen national and regional eco-environmental
security, China has designated permanent basic cropland, drawn red lines
for eco-environmental protection, delineated boundaries for urban devel-
opment, and set protection lines for all types of sea areas, in a coordinated
manner. It has established centralized control over the use of territorial
space and ensured that these lines are not crossed.
China has strengthened the management of key ecosystem service zones
and endeavored to prevent and control eco-environmental risks. County-
level administrative units that perform important ecological functions such
as water conservation, soil and water conservation, inhibiting winds, fixing
sand, and protecting biodiversity are designated as key ecosystem service
zones, which should focus on protecting the environment and providing eco-
environmental products and be restricted from large-scale industrialization
and urbanization. As a result, China’s natural ecosystems are generally stable
or improving, eco-environmental services have improved, and the supply of
eco-environmental products has continued to increase.
2. Strengthening eco-environmental conservation and restoration
Mountains, rivers, forests, farmland, lakes, grasslands and deserts
are communities of life. China has stepped up systematic, comprehen-
sive, and law-based environment governance, tackling problems at their
sources. Prioritizing protection and focusing on natural restoration, it has
vigorously pressed forward with the protection and restoration of ecosys-
tems, so as to build a solid national eco-environmental security barrier
and strengthen the foundations for the sustainable development of the
Chinese nation.
A new type of protected area (PA) system has been set up. PAs are
major platforms for eco-environmental conservation. China is develop-
ing a PA system with national parks as the mainstay, supported by nature
reserves and supplemented by nature parks. It has created its first batch
of five national parks – the Three-River-Source National Park, the Giant
Panda National Park, the Northeast China Tiger and Leopard National
Park, the Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park, and the Wuyishan
National Park. It is making steady progress in building national parks in
environmentally important regions. As of the end of 2021, nearly 10,000
PAs of various types and levels had been established, covering more than
17 percent of China’s land area, bringing under effective protection 90
percent of its natural terrestrial ecosystem types and 74 percent of key
state-protected wildlife species.
Setting up scientific eco-environmental conservation red lines
(ECRLs). ECRLs are the lifeline of national eco-environmental security.
China has brought functional areas of vital importance, exceedingly frag-
ile areas, and areas of potentially vital eco-environmental value within the
scope of the ECRL framework. More than 30 percent of China’s land area
– including integrated and optimized PAs – is now under the protection
of ECRLs. Through drawing ECRLs and drafting ecological protection
and restoration plans, the country has consolidated an overall eco-
environmental conservation configuration composed of Three Eco-zones and
Four Shelterbelts – the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Eco-zone, the Yellow River
Eco-zone (including the Loess Plateau Ecological Barrier), the Yangtze
River Eco-zone (including the Sichuan-Yunnan Ecological Barrier), and
the Northeast, North, South, and Coastal Shelterbelts.
Carrying out major projects for the conservation and restoration of key
national ecosystems. With a focus on major national eco-environmental
functional areas, ECRLs and PAs, China has launched projects for holistic
conservation and restoration of mountains, rivers, forests, farmland, lakes,
grasslands and deserts, taking comprehensive and systematic measures
Panel 2 Protected Area (PA) System
PAs are terrestrial or marine areas legally defined or confirmed by govern-
ments at various levels, assigned to carry out long-term conservation of important
ecosystems, natural relics, and natural landscapes as well as their natural resources,
ecological services and cultural values. In accordance with management goals and
efficacy, and profiting from international experience, China has classified PAs into
national parks, nature reserves and nature parks according to their environmental
value and protection sensitivity.
National parks are specific areas of land or sea set aside with the main goal
of protecting China’s unique ecosystems to achieve scientific conservation and ra-
tional utilization of natural resources. They are the most important of the country’s
natural ecosystems – those with the most distinctive natural landscapes, the finest
natural relics, and the richest biodiversity.
Nature reserves are areas with particular ecosystems, natural and concentrated
distributions of rare or endangered wildlife species, and natural relics of special
significance. Nature reserves are set up to guarantee the safety of the subjects under
protection, and maintain and restore populations of rare or endangered wild flora
and fauna species and the habitats on which they depend for survival.
Nature parks are areas containing important ecosystems, natural relics, and
natural landscapes of ecological, sightseeing, cultural or scientific value that can be
used sustainably. Their role is to ensure the effective protection of scarce natural
resources such as forests, oceans, wetlands, rivers, glaciers, grasslands and wild-
life, as well as the views, geological landforms, and cultural diversity they contain.
Nature parks include forest parks, geological parks, marine parks, wetland parks,
desert parks and grassland parks.
to deal with problems by addressing their root causes. It has carried out
shelterbelt and natural forest protection and restoration programs such
as the shelterbelt program in northeast China, north China and northwest
China, programs returning marginal farmland to forests and grasslands,
the program for ecological restoration of abandoned mines, the Blue Bay
environment improvement initiative, the coastal belts protection and
restoration program, the comprehensive management of the Bohai Sea
water environment, the conservation and restoration of mangrove for-
ests, and other restoration and rehabilitation projects of significant eco-
environmental importance. China has carried out large-scale afforestation
projects, steadily increased the area of forests, grasslands, wetlands, rivers
and lakes, and effectively reversed the trend of desertification.
From 2012 to 2021, 64 million hectares of trees were planted. Dur-
ing this period, desertification prevention and control was carried out over
18.53 million hectares of land, and 40 million hectares of land were im-
proved through sowing grass, and more than 800,000 hectares of wetland
were added or restored. In 2021, the forest coverage ratio hit 24 percent,
while the forest stock volume grew to 19.5 billion cubic meters. Both
figures represented 30 consecutive years of growth, making China the
country with the highest growth in forest resources and the largest area of
man-made forest. China is also the first country to realize zero net land
degradation – its desertified and sandified areas are both shrinking, and
this is helping the world to reach the global goal of zero net land degrada-
tion in 2030. Since 2000, China has led the world in greening the planet,
contributing around one fourth of the newly added green areas in the
world.
3. Promoting the green development of key regions
China gives full play to the guiding role of major strategies for re-
gional development and the implementation of these strategies, based
on prioritizing eco-environmental conservation and promoting green

development. It works to build the key regions into pioneers and models
in green development to boost green social and economic development
across the country.
Pushing for breakthroughs in environmental protection in the coordi-
nated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. The strategy for
the region’s coordinated development has been implemented, spurring the
integrated development of areas such as transport, environment, industry
Panel 3 Saihanba – From Desert to Oasis
Saihanba is located in the north of Hebei Province, about 300 kilometers to the
north of Beijing. In the 1950s it was a barren land ravaged by yellow sand with-
out so much as a tree for a bird to perch on. Sand whipped up by wind encroached
southward, threatening Beijing. To remedy this dire problem, shelter the capital
city from sand, and conserve water sources for Beijing and Tianjin, China set up
the Saihanba Mechanized Forest Farm in the early 1960s. An initial team of 369
started to reclaim the wasteland. Under sand-blotted sky and on this sand-locked
land, several dedicated Saihanba generations have worked without respite, building
the world’s largest man-made forest and creating a “desert-to-oasis” miracle. They
have created a green barrier safeguarding the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, and set-
ting an example for China and the world in terms of desertification control.
Today, the Saihanba Forest Farm covers an area of 76,733 hectares. It has a
growing forest stock volume of 10.4 million cubic meters, and every year it con-
serves and cleans 284 million cubic meters of freshwater, effectively preventing
soil erosion and laying a solid foundation for high-quality development in the
Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. The forest farm has also boosted seedling bases and
rural tourism, creating jobs for more than 4,000 locals and benefiting more than
40,000 people in the surrounding area. The forest farm has generated enormous
eco-environmental and social benefits, and changed the work and lives of the local
people for the better.
The green “Great Wall” built by the Saihanba Forest Farm has earned interna-
tional honors. In 2017, the forest farm won the UN Champions of the Earth Award,
and in 2021 it received the Land for Life Award from the UN.
and public services, and strengthening joint prevention and control of en-
vironmental problems. With the region as a focus, comprehensive efforts
have been made to address overexploitation of groundwater in north China,
with the groundwater level going down continuously since the 1980s
being reversed. In this region, Xiongan New Area is being built according
to forward-looking plans and high standards, with a focus on developing
it into a destination for entities relocated from Beijing as their functions
are non-essential to Beijing’s role as the capital. Xiongan will be built into
an eco-friendly exemplar city of high-quality green development with a
rational layout, a good balance of blue water, green areas, clean air, clear
skies and urban facilities. In 2021, in 13 cities in the region, 74 percent of
days had good air quality. This was an increase of 32 percentage points
compared with 2013. Beijing has set an example in air quality control for
the world.
Promoting well-coordinated environmental conservation and avoid-
ing excessive development while developing the Yangtze River Economic
Belt. The Yangtze River is the mother river of the Chinese nation, and
a powerhouse for China’s development. The restoration of the Yangtze
River’s eco-environment is a top priority. China is coordinating economic
development and environmental protection and building an economic belt
epitomizing green development and harmony between humanity and
nature.
Taking advantage of the opportunities offered by industrial inte-
gration, the Yangtze River Economic Belt is building a green industrial
system and accelerating its green economic transformation. A tough bat-
tle has been launched to protect and restore the eco-environment in the
Yangtze River Basin: Intense efforts have been made to carry out the “4+1”
project – the treatment of urban sewage and garbage, chemical pollution,
agricultural non-point source pollution, ship pollution and tailing pond
pollution; a comprehensive 10-year fishing ban in the Yangtze River Basin
has been implemented; action has been taken to regulate banks develop-
ment projects and remove illegal dykes. Since 2018, unauthorized structures
along 162 kilometers of the river banks have been demolished, more
than 12 square kilometers along the banks have been revegetated, and
4,533 hectares have been returned to water. The water quality at the state-
monitored sections of the mainstream of the Yangtze River has reached
Grade II level (the second best level) for the past two years.
The pioneering role of the Yangtze River Delta region in green de-
velopment. The construction of the Yangtze River Delta Integrated Green
Development Demonstration Zone will be accelerated, to explore ways to
translate eco-environmental strengths into social and economic benefits,
and ways for the region to transition from coordinated project execution
to regional integrated institutional innovation. With picturesque scenery,

a rich culture, specialty industries, and a cluster of innovation resources,
the region will lay a solid foundation for green development, and develop
into a hub for green and innovation-driven development.
Eco-environmental conservation and high-quality development in
the Yellow River Basin. Protecting the Yellow River is a long-term strat-
egy of fundamental importance to the Chinese nation. China has made
coordinated plans and carried out ecological protection and improvement
in the entire Yellow River Basin, including soil erosion and desertifica-
tion control in its upper and middle reaches and comprehensive treatment
of river courses and banks in the lower reaches. The sediment load of the
Yellow River has steadily fallen, which helps to ensure its safety. Water
availability has been a determining factor in urban and industrial develop-
ment, agriculture, and population distribution. A path of intensive water-
conservation has been followed so that water security has been effectively
ensured, water resources are used efficiently, and the ecology has im-
proved. Areas along the Yellow River are being protected in order to carry
forward and disseminate the Yellow River culture, develop specialty in-
dustries and nurture new industries and business models. This has raised
both the eco-environmental and economic value of the river, to the benefit
of the people.
Building a beautiful Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay
Area. China has vigorously improved the quality of the eco-environment
in the bay area, explored green and low-carbon urban construction and
operation models, and promoted sustainable development, making its skies
bluer, mountains greener, and water clearer. The area will enjoy a safe and
beautiful eco-environment, a stable society, and cultural prosperity.
4. Building a beautiful home with a pleasant living environment
Urban and rural areas are the carriers of human settlements and
activities. China integrates the philosophy of green development into urban
and rural construction, and promotes beautiful cities and beautiful coun-
tryside initiatives. With priority given to environmental pollution control,
China strives to improve the living environment to build a beautiful home
featuring lush mountains, green fields, singing birds, and blossoming
flowers.
Building beautiful cities featuring harmony between humanity and
nature. China has placed great emphasis on urban eco-environmental con-
servation and has adopted a people-centered approach to urbanization. It
has made sound plans for spaces for working, living and eco-environmental
conservation, and has worked to make cities livable, resilient and smart.
The aim is to build cities into beautiful homes where humanity and
nature coexist in harmony. In pursuing urbanization, China respects and
accommodates the requirements of nature. It has made use of mountains,
waters, and other unique landscapes to integrate cities into nature, so that
urban dwellers can enjoy the view and are reminded of their rural origins.
Efforts have been made to expand urban eco-environmental space through
construction of national garden cities and forest cities, as well as parks
and greenways in cities. With increased greenery coverage, the urban eco-
environment has been effectively restored. From 2012 to 2021, green
coverage of built-up urban areas increased from 39 percent to 42 percent,
and the per capita area of park greenery has increased from 11.8 square
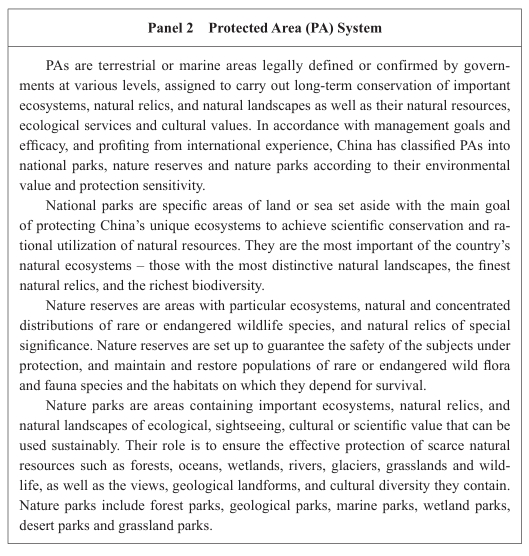
meters to 14.78 square meters. Great efforts have been made to construct
green and low-carbon buildings, and renovation of existing ones has been
promoted, contributing to increasingly higher energy efficiency.
Building a beautiful and harmonious countryside that is pleasant to
live and work in. Green development is a new driver of rural revitaliza-
tion, and China is exploring new paths for green development in rural
areas. It is actively developing new industries and new forms of busi-
ness such as eco-agriculture, rural e-commerce, leisure agriculture, rural
tourism, health, and elderly care, while advancing projects to protect
and restore ecosystems. These efforts allow China to approach its goal
of having strong agriculture and a beautiful and revitalized countryside.
China is continuing to redevelop the whole rural living environment and
steadily advancing the construction of modern and livable homes with
sanitary toilets in rural areas, strengthening the treatment and recycling of
domestic waste and sewage. As a result, more and more rural areas have
access to safe and clean water, paved roads, streetlights, and clean energy.
With an improved environment, the vast rural areas have become more
sustainable. Lush groves, orchards, and gardens of flowers and vegetables
set each other off, and the splendid pastoral scene is a treat for the eyes.
A beautiful countryside where the skies are blue, the lands are green, and
the waters are clear brings people delight with its scenic view. Greater ef-
forts have also been made to protect and utilize traditional villages and
carry forward their fine traditions, which have increased their cultural
charm.
Taking further steps to prevent and control pollution. The environ-
ment has a significant impact on quality of life. Green mountains display
beauty, and blue skies bring happiness. China is curbing pollution in a
law-based, scientific, and targeted way. Priority has been given to ad-
dressing the thorniest problems of air, water and soil contamination that
are of greatest concern to the public. Effective measures have been taken
to keep skies blue, waters clear, and land pollution-free. The mechanism
of coordinated prevention and control across regions and approaches in

dealing with heavy air pollution have achieved remarkable results. The
average PM2.5 density of China’s cities at prefecture level and above
dropped from 46 micrograms per cubic meter in 2015 to 30 micrograms
per cubic meter in 2021. On 87.5 percent of the days in 2021, people en-
joyed good air quality. China is making the fastest progress in air quality
improvement. With an accelerated pace in curbing industrial, agricultural
and domestic pollution sources, and in regulating water ecological sys-
tems, China has significantly reduced seriously polluted water bodies and
sub-standard water bodies, and the safety of drinking water is ensured.
In 2021, the proportion of surface water at or above Grade III in the
country’s five-tier water quality system reached 84.9 percent. China has
banned the import of foreign waste, fulfilling its goal of “zero import” of
solid waste while basically bringing the threat of soil contamination under
control. Brilliant blue skies are dotted with white clouds during the day;
when the sun sets, twinkling stars pattern the firmament. The shores are
Panel 5 Improving Urban and Rural Environmental Infrastructure
China attaches great importance to the construction of environmental infra-
structure and strives to address areas of weaknesses, optimize layouts, and improve
quality. It has improved facilities for sewage collection, treatment, and recycling,
and boosted the classification and treatment capacity of domestic waste. China
has also worked to ensure the safe and effective disposal of solid waste, hazardous
waste, and medical waste, promoted the integrated, intelligent, and green develop-
ment of environmental infrastructure, and built a system of environmental infra-
structure that integrates facilities and monitoring and supervising capabilities for
the treatment and disposal of sewage, garbage, solid waste, hazardous waste, and
medical waste. An environmental infrastructure network extending from cities to
towns and villages has taken shape. By the end of 2021, the sewage treatment capac-
ity of cities and counties has reached 247 million cubic meters per day, the incinera-
tion treatment capacity of urban domestic waste exceeded 770,000 tonnes per day,
and the harmless treatment rate of urban domestic waste was close to 100 percent.
green and the waters are clean, with fish gliding under the clear water.
People are breathing fresher air, drinking cleaner water, and eating safer
food. Living in a beautiful environment, people can truly feel the happi-
ness and beauty brought about by eco-environmental conservation.
III. Adjusting and Improving
the Industrial Structure
China is committed to the philosophy of innovative, coordinated,
green, open and shared development, and takes innovation-driven de-
velopment as the driving force to create new momentum and build new
strengths for economic development. China has placed rigid constraints
on the exploitation of resources and the environment to promote compre-
hensive adjustment of the industrial structure, and strengthened regional
cooperation to optimize the spatial configuration of industry. As a result,
China’s economy has registered a steady improvement in the quality of
development while maintaining a reasonable pace of growth.
1. Vigorously developing strategic emerging industries
China implements the innovation-driven development strategy. It
takes scientific and technological innovation as the driving force and
guarantee for adjustment of industrial structure and green and low-carbon
transition of the economy and society and regards strategic emerging in-
dustries as a key driver for economic development, reaping remarkable
economic and social benefits as a result.
China has intensified investment in scientific and technological
innovation. The nation’s gross domestic research and development (R&D)
spending grew from RMB1.03 trillion in 2012 to more than RMB2.8
trillion in 2021. Its R&D spending intensity, or the expenditure on R&D
as a percentage of its GDP, rose from 1.91 percent in 2012 to 2.44 percent
in 2021, approaching the average level of the Organization for Economic
Cooperation and Development (OECD) countries. Chinese enterprises’
investment in R&D has continued to increase, accounting for more than
76 percent of the country’s total R&D investment. By the end of 2021,
China’s energy conservation and environmental protection industry
owned 49,000 valid invention patents, and the new energy industry held
60,000, 1.6 and 1.7 times more than in 2017. From 2011 to 2020, the
number of patent applications filed by China for environment-related
technology inventions was close to 60 percent of the world total, making
it the most active country in environmental technology innovation.
Emerging technologies have become the main props of China’s eco-
nomic development. Thanks to accelerated efforts to implement emerg-
ing technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), big data, blockchain,
and quantum communication, new products and business forms including
intelligent terminals, telemedicine, and online education have been culti-
vated, and their role in boosting growth has continued to increase. China’s
digital economy ranks second in the world. During the 13th Five-year
Plan period (2016-2020), the average annual growth rate of the added
value of information transmission, software and information technol-
ogy services reached 21 percent. The internet, big data, AI, 5G and other
emerging technologies are deeply integrated with traditional industries,
facilitating the integration of advanced manufacturing with modern ser-
vices. The value-added output of high-tech and equipment manufacturing
in 2021 accounted for 15.1 and 32.4 percent of that of industries above
designated size, up 5.7 and 4.2 percentage points from 2012 respectively.
China is on the way to realize the transformation and upgrading from
“made in China” to “intelligent manufacturing in China”.
China’s green industries continue to grow. The renewable energy in-
dustry is growing rapidly, and China leads the world in the manufacture
of clean energy generation facilities for wind and photovoltaic power.
China produces more than 70 percent of the global total of polysilicon,
wafers, cells and modules. The quality and efficiency of the energy-saving
and environmental protection industries have continued to improve. China
has developed a green technical equipment manufacturing system covering
various sectors such as energy and water conservation, environmental
protection, and renewable energy. The manufacturing and supply
capacity of green technical equipment increases markedly while the cost
keeps dropping. Technology in the fields of energy and water conserva-
tion equipment, pollution control, and environmental monitoring meets
the highest international standards. New forms and models of business
continue to grow, such as comprehensive energy services, contract-based
energy and water management, third-party treatment of environmental
pollution, and comprehensive carbon emissions management services. In
2021, the output value of China’s energy conservation and environmental
protection industries exceeded RMB8 trillion. Extensive pilot projects
have been carried out at local level to explore methods and pathways to
realize the value of eco-environmental products. New models of eco-
friendly industry such as urban modern agriculture, leisure agriculture,
eco-environmental tourism, forest healthcare, boutique homestays, and
pastoral leisure complexes have witnessed rapid development.
2. Taking well-ordered steps to develop resource-based industries
China continues to expand supply-side structural reform and reverse
the extensive development model that relies heavily on resource con-
sumption at the cost of high pollution and emissions. With environmental
capacity as a rigid constraint, it has exerted tight control over the produc-
tion capacity of energy-intensive industries and industries with high emis-
sions or water consumption, in order to optimize its industrial structure.
Easing overcapacity and closing down outdated production facili-
ties. While protecting industrial and supply chains, China has taken ac-
tive and well-ordered steps to ease overcapacity and close down outdated
production facilities. Measures have been taken to curb industries that
over-exploit resources and cause environmental damage, such as steel, ce-
ment and electrolytic aluminum. A swap system has been introduced that
allows producers to open equal or lower amounts of new capacity in re-
turn for closures elsewhere. During the 13th Five-year Plan period (2016-
2020), China has removed more than 150 million tonnes of excess steel
production capacity and 300 million tonnes of excess cement production
capacity. Substandard steel products have been eliminated and almost all
outdated production capacity in industries such as electrolytic aluminum
and cement manufacturing has been removed.
China is resolved to stop the blind development of energy-intensive
projects with high emissions and outdated production techniques. It has
raised the entry threshold for some key industries in terms of land use,
environmental protection, energy and water conservation, technology, and
safety. A differentiated system has been introduced for energy-intensive
industries, covering differentiated electricity pricing, tiered electricity
pricing, and punitive electricity pricing. For energy-intensive projects
with high emissions and outdated production techniques, China applies
a list-based management approach involving classification and dynamic
monitoring. It resolutely investigates and punishes all projects that violate
laws or regulations. In areas with problems of water shortage or overcon-
sumption, restrictions are imposed on various types of new development
zones and projects requiring high water consumption.
3. Optimizing regional distribution of industries
Fully considering factors such as energy resources, environmental
capacity, and market potential, China promotes the convergence of some
industries in areas with more suitable conditions and greater potential for
development. To expedite the formation of a modern and efficient indus-
trial development configuration, it improves the distribution of productive
forces and expands the division of industries and coordination across re-
gions.
Working to bring about a rational distribution of raw material indus-
tries. China employs overall planning of resources such as coal and water
and takes into consideration environmental capacity. Several modern coal
chemical industry demonstration zones have been established in the cen-
tral and western regions to pilot projects for technology upgrading in the
coal chemical industry. A group of large-scale high-quality petrochemical
industry bases has been constructed in coastal areas to promote the safe,
green, intensive, and efficient development of the industry.
Expanding the division of industries and cooperation across regions.
China is seeking to establish and improve a benefit-sharing mechanism by
employing the comparative strengths of every region, each relying on its
own resources and environmental advantages, and on the foundations of
industrial development. Multi-type and multi-mechanism industrial divi-
sion and coordination have been strengthened, along with cooperation be-
tween the east and the central and western regions, creating a framework
of coordination, complementarity of strengths, and common development.
Transferring industries and cooperation across regions are measures that
help to break through the environmental and resource constraints that sti-
fle industrial development. They also make room for the development of
high-tech industries in the eastern region and propel the industrialization
and urbanization process of underdeveloped areas in the central and west-
ern regions, improving the balance and strengthening the coordination of
regional development.
IV. Extensive Application of
Green Production Methods
China has accelerated the building of a green, circular, and low-carbon
economy. It practices green production methods, promotes the energy
revolution, the economical and intensive use of resources, and cleaner
production, and pursues synergy in the reduction of pollution and carbon
emissions. All these efforts have contributed to the coordinated develop-
ment and balanced progress of the economy, society, and environmental
protection.
1. Promoting the green transformation of traditional industries
In order to build a green, circular, and low-carbon production system,
China has integrated the concept of green development into the entire life
cycles of industry, agriculture and the service sector. To conserve energy,
reduce emissions, raise efficiency, and facilitate the comprehensive green
transformation of traditional industries, China has encouraged innovations
in technology, models, and standards.
Promoting the green development of industry. China is committed to
establishing a green manufacturing system, and creating green factories,
green industrial parks, green supply chains, and green product evaluation
standards. In order to accelerate the building of green industrial chains
and supply chains, China provides guidance for enterprises to achieve in-
novations in the design of green products and adopt green, low-carbon
and eco-friendly processes and equipment, and optimizes the spatial lay-
out of enterprises, industries and infrastructure in industrial parks. Fol-
lowing the principles of “coupling of industries, extended responsibility
of enterprises, and circular use of resources”, it has promoted the transfor-
mation of industrial parks, circular combination of industries and circular
production in enterprises. China has transformed its major industries to
achieve clean production, and carried out comprehensive inspections of
clean production. It has promoted digital transformation across the board.
The digital control rate of key processes in key areas increased from 24.6
percent in 2012 to 55.3 percent in 2021, and the penetration rate of digi-
tal R&D and design tools increased from 48.8 percent to 74.7 percent in
the same period. By the end of 2021, China hosted a total of 2,783 green
factories, 223 green industrial parks, and 296 green supply chain manage-
ment enterprises. The manufacturing sector has been significantly upgrad-
ed for green production.
Transforming the production methods of agriculture. China has cre-
ated new systems and mechanisms for the green development of agricul-
ture, expanded the functions of agriculture, explored the diversified rural
values, and strengthened the protection and efficient use of agricultural
resources. It has gradually improved the farmland protection system and
the system of fallowing and crop rotation, put permanent basic cropland
under special protection, and thereby made initial progress in containing
the decline in the size of farmland. It has steadily advanced the conserva-
tion of chernozem soil. The quality of farmland has been upgraded steadily
throughout the country. Measures have been taken to save water for agri-
cultural irrigation and reduce the volume of chemical fertilizers and pesti-
cides used by targeting higher efficiency. In 2021, the irrigation efficiency
was raised to 0.568. China has developed a circular agricultural economy
by promoting circular agricultural production modes – integrating planting
and breeding with processing, farming and animal husbandry with fishing,
and production and processing with marketing. It has increased the utili-
zation of agricultural waste as a resource. It has taken a coordinated ap-
proach to promoting green and organic agricultural products, products with
quality certifications and those with geographical indications, cultivating
new breeds, improving product quality, fostering agricultural brands and
standardizing agricultural production. China has implemented programs
to protect agricultural products with geographical indications. There are
now 60,000 types of green food and organic agricultural products across
the country. The quality and safety standards of agricultural products have
been steadily upgraded. The supply of high-quality agricultural products
has increased significantly, which has effectively contributed to the up-
grading of the whole industry, and generated higher incomes for farmers.
Advancing the green transformation of the service sector. China
has actively cultivated green firms of business circulation, and launched
a campaign to create green shopping malls. Nationwide, a total of 592
green shopping malls had been built by the end of 2021. China has contin-
ued to improve the energy efficiency of the information service industry,
with some world-leading green data centers. To accelerate the reduc-
tion, standardization and recycling of express delivery packages, it has
upgraded and improved the express delivery packaging standard system.
To promote the green development of e-commerce enterprises, it has
given guidance for producers and consumers to use renewable and degra-
dable express delivery packages. By the end of 2021, 80.5 percent of
e-commerce parcels were free of secondary packaging, all express delivery
packages were sealed with thinner (45mm) tape, and all transit bags used
in the sector were renewable.
China has promoted the green development of the convention and
exhibition industry by formulating green standards and facilitating the
repeated use of facilities. China has significantly reduced paper usage by
introducing electronic railway tickets nationwide and encouraging elec-
tronic invoicing. In the catering industry, disposable tableware is being
phased out. Guest houses and hotels have been encouraged not to offer
disposable items as part of their services.
2. Promoting green and low-carbon energy
China applies the principle of building the new before discarding
the old in a well-planned way. With growing capacity to ensure energy
supply, it has moved faster to build a new energy system. The propor-
tion of clean energy sources has increased significantly. Success has been
achieved in the green and low-carbon transformation of the country’s en-
ergy mix.
Vigorously developing non-fossil energy. China has made rapid pro-
gress in building large-scale wind and photovoltaic power stations on in-
fertile and rocky terrain and in deserts. It has steadily developed offshore
wind farms, actively promoted rooftop photovoltaic power generation in
urban and rural areas, and encouraged distributed wind power generation
in rural areas. China has built a structured matrix of large hydropower
stations in the basins of major rivers, especially those in the southwest.
In accordance with local conditions, it has developed solar, biomass,
geothermal and ocean energy, and power generation through urban solid
waste incineration. It has developed nuclear power in a safe and orderly
manner. Committed to innovation-driven development, China has worked
on developing hydrogen energy. It has accelerated the construction of a
new power system to adapt to the steady increase in the proportion of new
energy. To promote the efficient use of renewable energy, it has carried
out appraisals of relevant parties’ performance in meeting the set goals for
consumption of power generated from renewable energy. The proportion
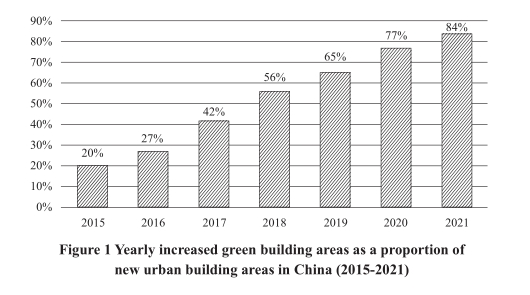
of clean energy sources in total energy consumption increased from 14.5
percent in 2012 to 25.5 percent by the end of 2021, and the proportion
of coal decreased from 68.5 percent to 56 percent over the same period.
The installed capacity of renewable energy was more than one billion
kilowatts, accounting for 44.8 percent of China’s overall installed capac-
ity. The installed capacity of hydropower, wind power, and photovoltaic
power each exceeded 300 million kilowatts, all ranking the highest in the
world.
Advancing the clean and efficient use of fossil energy. To promote
the clean and low-carbon development of coal-fired power, China has up-
graded coal-fired power plants to conserve resources, reduce carbon emis-
sions and make their operation more flexible, and transformed heating
facilities. It has implemented stricter energy-saving standards for newly-
installed coal-fired generating units. The efficiency and pollutant con-
trol levels of these units are on par with the most advanced international
standards. China has promoted clean end-use energy by replacing coal
with natural gas, electricity, and renewable energy. It has actively support-
ed clean heating in winter in northern China. It has made the use of natu-
ral gas more efficient in urban areas, as well as in industrial fuel, power
generation, and transport, and promoted natural gas combined cooling,
heating, and power (CCHP). It has launched a campaign to upgrade the
quality of refined oil products. In less than 10 years China achieved the
upgrading that took developed countries 30-plus years, and its refined oil
products are now of the best quality by international standards. As a re-
sult, vehicle pollutant discharge has been effectively reduced.
3. Building a green transport network
The transport sector is one that consumes a large amount of energy
and generates significant pollutant and greenhouse gas emissions. This

is an area that deserves more attention in the pursuit of green develop-
ment. By upgrading the energy efficiency of transport equipment, China
has accelerated the building of a green transport network, with optimizing
the structure of energy consumption and improving the efficiency of or-
ganization as its priorities, so that transport will be more eco-friendly, and
travel will be more low-carbon.
Optimizing the structure of transport. China has accelerated the con-
struction of special railway lines, promoted the shift of freight transport
from road to railway and waterway, and encouraged intermodal transport.
In 2021, the railway and waterway freight volume accounted for 24.56
percent of the total in China, an increase of 3.85 percentage points over
Panel 6 Green Electricity for the 2022 Beijing Winter Olympics
The Beijing Winter Olympic Games opened on February 4, 2022. These games
were different from their predecessors in that green electricity was used in all
the 26 venues in the three competition zones – the first time in the history of the
Olympic Games that all the venues had been powered by green electricity. Green
electricity served all the purposes of the Beijing Winter Olympic Games – venue
lighting, ice surface maintenance, production of artificial snow, TV broadcasting,
timekeeping, security and logistical support. China put into action the concept of
sustainable development it advocated when bidding for the Games. To supply the
Games with green electricity, China built a large number of wind and PV power
projects in Beijing, Zhangjiakou and other regions, and launched the Zhangjiakou-
Beijing flexible HVDC pilot project, to transmit clean electricity to the Games ven-
ues. This not only met the demand of the Games for lighting, operations, transport
and other purposes, but also raised by a substantial margin the share of clean energy
consumption in Beijing and surrounding areas. Seizing the opportunities presented
by hosting the green Winter Olympic Games, China has realized the large-scale
transmission, grid-connection, and uptake of clean energy, accumulating valuable
practical experience for the further development of clean energy, and demonstrating
its confidence and determination in achieving the goals of carbon emissions peak-
ing and carbon neutrality.
2012. China has also emphasized the strategy of giving priority to urban
public transport. By the end of 2021, there were 275 urban rail transit
lines in operation in 51 cities, with a total track length of more than 8,700
kilometers. The length of exclusive bus lanes increased from 5,256 kilo-
meters in 2012 to 18,264 kilometers in 2021.
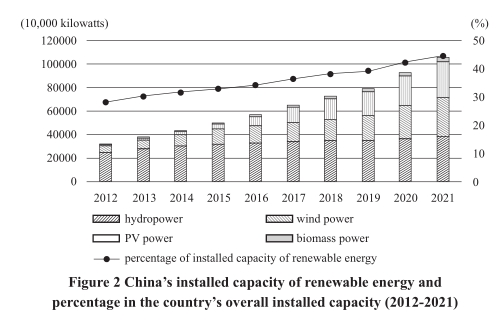
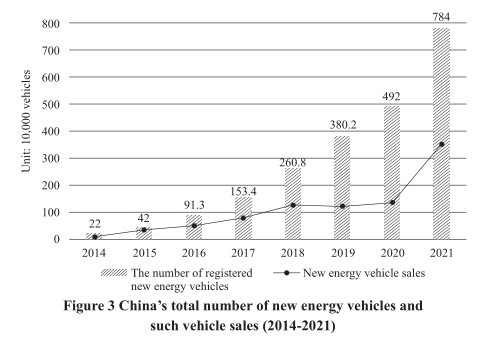
Promoting the green transformation of transport vehicles. China
has vigorously promoted the use of new-energy vehicles in public trans-
port, taxi service, environmental sanitation, logistics, distribution, civil
aviation, airports, and Party and government institutions. By the end of
2021, the number of China’s registered new energy vehicles had reached
7.84 million, accounting for about half of the global figure. There were
508,900 new energy buses, accounting for 71.7 percent of the total num-
ber of buses in China. There were 207,800 new energy taxis. China has
continued the green transformation of mobile railway equipment. The
proportion of internal combustion locomotives decreased from 51 percent
in 2012 to 36 percent in 2021. China has also updated the pollutant dis-
charge standards for motor vehicles, promoted the use of liquefied natural
gas (LNG) powered boats and transformation of shore power facilities,
and accelerated the transformation or elimination of obsolete vehicles and
boats. Since 2012, more than 30 million yellow-label vehicles with high
emissions have been eliminated, and 47,100 obsolete inland river boats
have been re-engineered or mothballed.
Upgrading transport infrastructure for green development. China has
initiated a special program for the construction of green highways, and
the recycling of waste road surface materials. By the end of 2021, more
than 95 percent of the waste materials from expressways and 80 percent
of the waste materials from national and provincial highways had been
recycled. China has steadily improved afforestation along its roads. Green
belts have been built along 570,000 kilometers of its trunk roads, about
200,000 kilometers more than in 2012. China has continued the electrifi-
cation of its railways, with the proportion of electric railways increasing
from 52.3 percent in 2012 to 73.3 percent in 2021. It has also built more
green port and road transport support facilities. By the end of 2021, five
types of shore power facilities had been built in 75 percent of the special-
ized berths of major ports, and 13,374 charging piles had been built in ex-
pressway service areas – the highest number in the world.
4. Promoting the economical and intensive use of resources
As a country with a great demand for resources, China has acceler-
ated the fundamental change in the way resources are utilized. To make a
major contribution to the sustainable development of global resources and
the environment, and to ensure a happy life for the people today as well
as sufficient resources to meet the needs of future generations, China tries
to obtain the maximum social and economic benefits at a minimum cost
in resources and the environment.
Improving the efficiency of energy use. China is exercising better
control over the amount and intensity of energy consumption, particularly
the consumption of fossil fuels. It has vigorously promoted technical,
managerial, and structural energy conservation, to constantly improve the
efficiency of energy use. It has initiated campaigns for all industrial enter-
prises, especially the big consumers of energy, to save energy, reduce car-
bon emissions, and improve the efficiency of energy use. The “forerunners”
have been encouraged to play an exemplary role for other enterprises.
China has organized the transformation of energy-intensive industries
such as steel, power generation, and chemicals, to help them save energy
and reduce carbon emissions. It has also strengthened the energy-saving
management of key energy consumers, to enable large and medium-sized
enterprises in key industries to reach advanced international levels in en-
ergy efficiency. Since 2012, China’s average annual economic growth of
6.6 percent has been supported by an average annual growth of 3 percent
in energy consumption, and the energy consumption per RMB10,000 of
GDP in 2021 was 26.4 percent lower than in 2012.
Improving the efficiency of water utilization. China has imposed in-
creasingly rigid constraints on water use. Industrial and urban configura-
tions are determined scientifically in accordance with water availability.
China has launched nationwide water-saving campaigns to control the
total amount and intensity of water consumption. It has upgraded water-
saving technologies for industries with high water consumption, and pro-
moted highly water-efficient irrigation for agriculture. It has advocated
the building of water-saving cities, established a water efficiency labeling
system, introduced certification standards for water conservation prod-
ucts, and promoted the use of water-saving products and appliances. The
comprehensive per capita water consumption in cities is falling steadily.
China has also incorporated unconventional water sources, such as re-
claimed water, desalinated seawater, collected rainwater, brackish water,
and mine water, into the unified allocation of water resources, which has
effectively eased the strain on demand in areas with a shortage of water.
Water consumption per RMB10,000 of GDP in 2021 was 45 percent low-
er than in 2012.
Strengthening the economical and intensive use of land. China has
improved the standards for urban and rural land use. The designation,
standards and approval of land use for all kinds of construction projects
are strictly controlled, and the economical and intensive use of land in the
construction of transport, energy, and water infrastructure is encouraged.
China has strengthened the management of rural land, and promoted the
economical and intensive use of rural land for collective construction pro-
jects. It has also established mechanisms for coordinating the use of exist-
ing land resources and made the arrangements for additional resources,
and for recovering idle land, in order to put all existing land resources to
good use. From 2012 to 2021, the area of land designated for construction
projects per unit of GDP decreased by 40.85 percent.
Making scientific use of marine resources. China has strictly con-
trolled land reclamation from the sea. It has prohibited all coastal recla-
mation activities except those for major national projects, and dealt with
problems left over from history in this regard with different approaches.
It has established a control system to retain natural shorelines, and carried
out classified protection and economical utilization of them. It has strictly
protected uninhabited islands at sea and minimized their development and
utilization.
Ensuring the comprehensive use of resources. China has advocated
the construction of green mines, promoted green exploration and exploi-
tation, and worked to increase the recovery rate, processing recovery rate,
and multipurpose utilization rate of major mineral resources. A total of
1,101 state-level green mines have been built. China has selected a total
of 100 pilot projects and 100 backbone enterprises to promote the compre-
hensive use of resources and started the construction of national demon-
stration bases for recovering mineral resources from city waste. It has also
updated the waste material collection network, coordinated the recycling
of waste resources, and improved the processing and utilization of renew-
able resources. In 2021, 385 million tonnes of nine renewable resources –
waste iron and steel, copper, aluminum, lead, zinc, paper, plastic, rubber,
and glass – were recycled for new purposes.
V. Eco-Friendly Living Becomes
the Prevailing Ethos
Green development requires everyone’s efforts, and each of us can
promote and practice green living. China actively promotes the values
and ideas of eco-environmental conservation, raises public awareness to
conserve resources and protect the eco-environment, and advocates the
practice of a simpler, greener, and low-carbon lifestyle, creating a condu-
cive social atmosphere for jointly promoting green development.
1. Continuing progress towards raising conservation awareness
China places particular emphasis on cultivating its citizens’ conser-
vation awareness. It organizes systematic publicity and other awareness-
raising activities in this regard, and advocates a social environment and
lifestyle of diligence and frugality. Publicity activities themed on National
Energy-Saving Publicity Week, China’s Water Week, National Urban
Water-Saving Week, National Low-Carbon Day, National Tree-Planting
Day, World Environment Day, the International Day for Biological Di-
versity, and Earth Day, are organized on a regular basis to encourage and
persuade the whole of society to engage in green development activities.
The idea of eco-friendly living has become widely accepted in families,
communities, factories, and rural areas. Material on green development
has been incorporated into China’s national education system through
compiling textbooks on eco-environmental conservation and carrying out
education in primary and secondary schools on the condition of national
resources including forests, grasslands, rivers and lakes, land, water and
grain. Respect for and love of nature have been advocated. Environmental
Code of Conduct for Citizens (for Trial Implementation) was published to
guide the public to follow a green lifestyle. As a result, a culture of eco-
logical and environmental protection has joined the mainstream and been
cherished by all.
2. Widespread initiatives to promote eco-friendly lifestyles
China has launched initiatives to promote the building of resource-
conserving Party and government offices, and develop eco-friendly
families, schools, communities, transport services, shopping malls, and
buildings, popularizing eco-friendly habits in all areas including cloth-
ing, food, housing, transport, and tourism. To date, 70 percent of Party
and government offices at and above county level are now committed to
resource conservation, almost 100 colleges and universities have realized
smart monitoring of water and electricity consumption, 109 cities have
participated in green transport and commutes initiatives. Household waste
sorting has been widely promoted in cities at or above prefecture level.
Much progress is being made as residents gradually adopt the habit of
sorting their waste. The Law of the People’s Republic of China on Food
Waste has been enacted, and initiatives launched to promote food saving
and curb food waste including a “clean plate” campaign on a large scale,
which have yielded remarkable results as more people are saving food.
3. Growing market of green products
China has actively promoted energy-saving and low-carbon products
such as new-energy vehicles and energy-efficient household appliances. It
has provided tax reductions or exemptions and government subsidies for
new-energy vehicles and continued to improve charging infrastructure. As
a result, the sales of new-energy vehicles have rapidly risen from 13,000
in 2012 to 3.52 million in 2021. For the seven years since 2015, China
has ranked first in the world in the production and sales of new-energy ve-
hicles. In addition, China has steadily improved the certification and pro-
motion system for green products and the green government procurement
system, implemented an energy efficiency and water efficiency labeling
system to encourage the consumption of green products. It has promoted
the construction of green infrastructure in the circulation sector such as
green shopping malls, and supported new business models such as the
sharing economy and second-hand transactions. There is a richer variety
of green products and a growing number of people who spend on green
products.
VI. Improving the Institutions and
Mechanisms for Green Development
Sound institutions and mechanisms are essential to green develop-
ment. With this understanding, China has stepped up efforts to create an
eco-environmental conservation system based on clear orientation, sound
decision-making, effective implementation, and strong incentives, and
continued to improve government performance in promoting green devel-
opment. This provides a solid guarantee for the realization of the coun-
try’s green development goals.
1. Strengthening the rule of law
China is committed to the rule of law in pursuing progress in eco-
environmental conservation. It has written into its Constitution eco-
environmental improvement and conservation, and promulgated and/or
revised laws such as the Yangtze River Protection Law, the Yellow River
Protection Law, the Land Administration Law, the Forest Law, the Grass-
land Law, the Wetland Protection Law, the Environmental Protection Law,
the Law on Environmental Protection Tax, the Law on the Prevention and
Control of Atmospheric Pollution, the Law on the Prevention and Control
of Water Pollution, the Law on the Prevention and Control of Soil Pollu-
tion, and the Nuclear Safety Law. A legal system for eco-environmental
conservation that covers all key areas, all types of resources, and all envi-
ronmental factors has taken shape. China has also made consistent efforts
to refine green development standards for key areas – more than 3,000
such standards have been formulated or amended.
To better investigate and strictly punish violations of laws and regu-
lations concerning natural resources and the eco-environment, China has
reformed the system that places the monitoring, supervision, and law
enforcement activities of environmental protection bodies below the pro-
vincial level under the leadership of the same type of bodies at the imme-
diate higher level. To strengthen coordination between the criminal justice
system and law enforcement by government departments, China has es-
tablished a system for procuratorates, courts, public security organs, and
government departments responsible for coordinated law enforcement for
environmental protection, enabling them to share relevant information, is-
sue case briefings, and transfer cases among them. This has built a strong
synergy for the investigation and punishment of environmental crimes,
and provided powerful legal safeguards for green development.
2. Tightening supervision and management
China has improved the performance evaluation system for green de-
velopment, and taken strict measures to ensure that enterprises fulfill their
principal responsibilities and that the government performs the duty of
supervision in pursuing green development. GDP growth is no longer the
sole criterion for the assessment of the development of regions or the per-
formance of officials. Instead, binding targets concerning resources and
the environment are set for economic and social development, and a more
balanced assessment system for economic and social development is in
progress – one that measures the use of resources, energy consumption,
environmental damage, and the eco-environmental impact. This allows
assessment to play its full guiding role in promoting green development.
China has put in place an accountability system for leading officials,
and formulated and/or revised a number of CPC regulations, including the
Measures for Holding Leading Officials of the Party and the Government
Accountable for Environmental Damage (for Trial Implementation), the
Regulations on Central Environmental Inspections, and the Regulations
on the Auditing of Natural Resource Assets for Leading Officials at the
End of Their Tenures (for Trial Implementation). These are designed to
ensure that Party committees and governments assume equal responsibili-
ties for environmental protection, that leading officials perform their en-
vironmental protection responsibilities with diligence, in addition to their
other prescribed duties, and that they are held accountable when they fail
to do so. China mandates end-of-tenure auditing of natural resource as-
sets for leading officials, and imposes lifelong accountability for environ-
mental damage. By implementing the central environmental inspection
system, China has ensured that all parties concerned truly fulfill their re-
sponsibilities for environmental protection, and has solved many environ-
mental issues of pressing public concern.
3. Improving market-based mechanisms
China is creating institutions and mechanisms for green development
through which the government provides strong guidance, enterprises are
fully engaged, and the market plays an effective role, thereby generating
society-wide enthusiasm and participation. It has introduced new meas-
ures to improve the pricing mechanisms in key areas such as water and
energy saving, sewage and waste treatment, and air pollution control,
adopted more than 50 preferential policies to cut taxes and fees, encour-
aged better resource allocation, and supported conservation and efficient
use of resources to advance green development. China has enforced a
unified registration system for ownership of natural resources and an eco-
environmental conservation compensation system that covers forests,
grasslands, wetlands, deserts, water bodies and farmland. It is working
on mechanisms for realizing the market value of ecosystem goods and
services. China also encourages and supports private investment in envi-
ronmental conservation and rehabilitation.
On the base of a reasonable ceiling for total consumption, China
has established initial allocation and trading systems for water, energy,
pollution, and carbon permits. With the opening of the national carbon
emissions trading market and trials in green electricity trading, progress
is being made in allowing the market to play a fundamental role in the

allocation of eco-environmental resources.
In order to boost green finance, China has developed a multi-level
market and a portfolio of green financial products, such as green credit,
green bonds, green insurance, green funds, and green trust. At the end of
2021 China’s green loan balance in RMB and foreign currencies stood
at RMB15.9 trillion, and its outstanding green bonds at RMB1.1 trillion,
both ranking among the largest in the world.
VII. Building the Earth into a Beautiful Home
Green development and eco-environmental progress are the re-
sponsibility of all humanity. China has always been a major participant,
contributor, and torchbearer in the global movement for building an eco-
civilization. It firmly safeguards multilateralism, and is actively forging
an international eco-environmental governance pattern in which countries
align their interests and share their rights and responsibilities. This is how
China does its part in pursuing the sustainable development of humanity.
1. Participating in global climate governance
Following the principles of equity, common but differentiated re-
sponsibilities and respective capabilities, China has acted in accordance
with the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, ac-
tively participated in global climate negotiations in a constructive manner,
and made historic contributions to the conclusion and implementation of
the Paris Agreement. In doing so, it helps to build a fair, rational, and mu-
tually beneficial global climate governance system.
China has reinforced the effort to achieve its Nationally Determined
Contributions (NDCs). It will make the steepest cuts in the world to the
intensity of its carbon emissions, and complete the process from carbon
emissions peaking to carbon neutrality in the shortest span of time. This
fully demonstrates its strong sense of responsibility as a major country.
China is also an active participant in South-South cooperation on
climate change. Since 2016, working in other developing countries, it has
launched 10 low-carbon demonstration zones, 100 projects for climate
change mitigation and adaption, training sessions on climate change re-
sponse for 1,000 people, and more than 200 foreign assistance programs
on climate change.
International cooperation on climate change may encounter difficul-
ties and setbacks, but China will remain committed to improving global
climate governance and taking solid actions. As always, it will work with
firm resolve towards the goals of carbon emissions peaking and carbon neu-
trality, actively participate in international cooperation on climate change,
engage in international negotiations on climate change in a constructive
manner, and do everything in its power to support and assist other devel-
oping countries in this realm. In doing so, China will continue to contrib-
ute to global efforts to tackle the grave challenge of climate change.
2. Building a green Belt and Road
China is committed to working with other countries on promoting
green development under the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), making it a
green initiative. In order to establish a cooperation mechanism for green
and low-carbon development under the BRI, China has signed an MoU
with the United Nations Environment Programme on building a green
Belt and Road, and reached more than 50 cooperation agreements on eco-
environmental conservation with relevant countries and international
organizations. It has also launched the Initiative for Belt and Road Partner-
ship on Green Development with 31 countries, established the Belt and
Road Energy Partnership (BREP) with 32 countries, led the creation of
the Belt and Road Initiative International Green Development Coalition
(BRIGC), founded the BRI Green Development Institute, and launched
the BRI Environmental Big Data Platform.
China has helped other participants in the BRI to build up their en-
vironmental governance capacity and improve their people’s well-being.
It also helps these countries in training personnel for green development,
having trained 3,000 people from more than 120 countries under the
Green Silk Road Envoys Program. China formulated the Green Invest-
ment Principles for the Belt and Road to encourage such investments in
related regions. Concurrently, Chinese enterprises have funded renewable
energy projects in other BRI countries, and helped them build a number
of major clean energy facilities. All these efforts have boosted green de-
velopment in these countries.
3. Carrying out extensive bilateral and multilateral cooperation
China has taken active steps to advance practical cooperation on sav-
ing resources and protecting the eco-environment. It successfully hosted
the first part of the 15th meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the

Convention on Biological Diversity (COP15) and the 14th meeting of the
Conference of the Contracting Parties to the Ramsar Convention on Wet-
lands. China is an active participant in cooperation on energy transition
and energy efficiency under the frameworks of G20, China-ASEAN part-
nership, ASEAN Plus Three, East Asia Summit, Forum on China-Africa
Cooperation, BRICS, Shanghai Cooperation Organization, and Asia-
Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC). It took the lead in formulating the
G20 Energy Efficiency Leading Programme, a key outcome of the G20
Hangzhou Summit. It has put into action the Global Development Initia-
tive, and worked for the establishment of the Global Clean Energy Coop-
eration Partnership.
China has also carried out cooperation with other countries and re-
gions – including India, Brazil, South Africa, the United States, Japan,
Germany, France, and ASEAN countries – in the fields of energy con-
servation, environmental protection, clean energy, response to climate
change, biodiversity protection, prevention and control of desertification,
and conservation of marine and forest resources.
China also supports international organizations, including the UN
agencies, Asian Development Bank, Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank,
New Development Bank, Global Environment Facility, Green Climate
Fund, International Energy Agency, and International Renewable Energy
Agency, in carrying out technological assistance, capacity building and
trial programs for green and low-carbon development in key sectors such
as industry, agriculture, energy, transport, and urban-rural development.
Through these efforts China has made a significant contribution to advanc-
ing sustainable development worldwide.
Conclusion
China has embarked on a new journey to build itself into a modern
socialist country in all respects and advance the rejuvenation of the Chinese
nation. Harmony between humanity and nature is an important feature of
China’s modernization.
The just-concluded 20th CPC National Congress has made strategic
plans for China’s future development which will help to create a better
environment with greener mountains, cleaner water, and clearer air. China
will keep to the path of green development, continue to build an eco-
civilization, and strive to realize development with a higher level of qual-
ity, efficiency, equity, sustainability and security. We will make “green”
a defining feature of a beautiful China and allow the people to share the
beauty of nature and life in a healthy environment.
The earth is our one and only home, and humanity and nature form a
community of life. It is the common responsibility of all countries to protect
the environment and promote sustainable development. China stands ready
to work with the international community to advance eco-environmental
conservation, promote green development, protect the green earth, and
build a cleaner and more beautiful world.
-
Xi urges teachers to contribute more to realizing national rejuvenation
Xi urges teachers to contribute more to realizing national rejuvenation
-
Chinese premier calls for advancing economic globalization, unity within G20
Chinese premier calls for advancing economic globalization, unity within G20
-
China's opening-up, improved business environment garner foreign investors' confidence
China's opening-up, improved business environment garner foreign investors' confidence
-
Russian-Chinese forum "Rostki" boosts practical cooperation
Russian-Chinese forum "Rostki" boosts practical cooperation